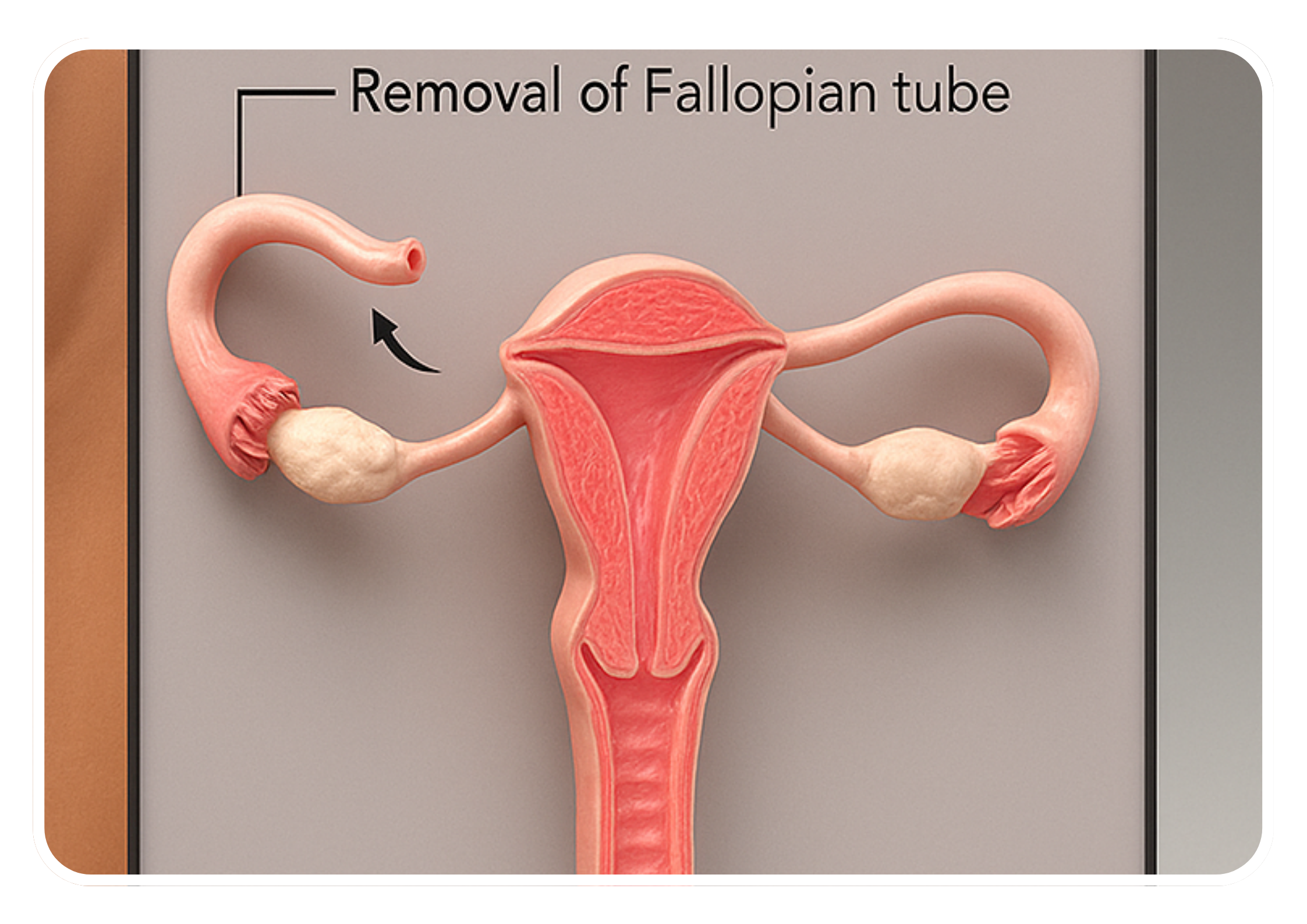
Indications
Laparoscopic salpingectomy-tubectomy is indicated for women who have completed their desired family size and wish to permanently prevent having any tubal pathology like hydrosalpinx, pyosalpinx or tubal ehotopic pregnancy. It is a highly effective form of contraception and is considered a permanent sterilization procedure. Additionally, bilateral salpingectomy may be recommended for women at high risk of ovarian cancer, as it has been shown to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer by removing the fallopian tubes, where some ovarian cancers originate.
Preoperative Evaluation
Before undergoing laparoscopic salpingectomy-tubectomy, patients typically undergo a comprehensive preoperative evaluation, including:
- Medical History Review: Assessment of the patient’s overall health and any underlying medical conditions.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical check-up.
- Imaging study to diagnose any tubal pathology by Ultrasound(USG) or MRI.
- Counseling: Discussion regarding the risks, benefits, and alternatives to tubal sterilization. Counseling should also include discussion of other contraceptive options and the irreversibility of tubal sterilization.
Surgical Technique
Laparoscopic salpingectomy-tubectomy is performed under general anesthesia in an operating room equipped for laparoscopic surgery. The procedure involves the following steps:
- Anesthesia: The patient is placed under general anesthesia.
- Incisions: Several small (typically 0.5 to 1 cm) incisions are made in the abdomen, usually around the belly button and lower abdomen.
- Trocar Placement: Trocars (hollow tubes) are inserted through the incisions to provide access for the laparoscope and specialized instruments.
- Visualization: A laparoscope is inserted through one of the trocars to provide a magnified view of the pelvic organs, including the fallopian tubes. Carbon dioxide gas is used to inflate the abdominal cavity, creating space for visualization and instrument manipulation.
- Salpingectomy-Tubectomy: The fallopian tubes are identified, isolated, and either removed (salpingectomy) or occluded (tubal occlusion) to prevent the passage of eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Removal of the fallopian tubes (salpingectomy) may be preferred for women at high risk of ovarian cancer or for those undergoing the procedure for gynecological reasons. Alternatively, tubal occlusion techniques such as tubal ligation clips, rings, or electrocoagulation may be used for contraception.
- Closure: After the fallopian tubes have been removed or occluded, any bleeding vessels or defects in the abdominal wall are carefully inspected and controlled. The small incisions are then closed with sutures or surgical glue, and dressings may be applied.
Advantages
- Highly Effective: Laparoscopic salpingectomy-tubectomy is a highly effective form of contraception, with a very low failure rate.
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure involves smaller incisions, resulting in less postoperative pain, reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
- Potential Cancer Risk Reduction: Bilateral salpingectomy has been shown to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer by removing the fallopian tubes, where some ovarian cancers originate.
Considerations
- Irreversibility: Laparoscopic salpingectomy-tubectomy is considered a permanent sterilization procedure and is not easily reversible. Patients should be counseled regarding the irreversible nature of tubal sterilization and the need for careful consideration before undergoing the procedure.
- Contraceptive Counseling: Patients considering laparoscopic salpingectomy-tubectomy should receive comprehensive contraceptive counseling to ensure that they understand the risks, benefits, and alternatives to sterilization. Counseling should also include discussion of other long-term reversible contraceptive options for women who may have future fertility desires.
- Surgical Expertise: Laparoscopic salpingectomy-tubectomy requires specialized training and expertise in laparoscopic techniques. Surgeons should be proficient in minimally invasive surgery and familiar with the nuances of tubal sterilization to ensure optimal outcomes.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic salpingectomy-tubectomy is an effective and permanent form of contraception for women who have completed their desired family size. When performed by experienced surgeons in appropriately selected patients, laparoscopic salpingectomy-tubectomy offers the advantages of minimally invasive surgery, reduced morbidity, and reliable contraception. Additionally, bilateral salpingectomy may provide the added benefit of reducing the risk of ovarian cancer in certain populations.
At Bliss IVF, our team of skilled surgeons and healthcare providers is dedicated to offering the highest standard of care. We are committed to helping you understand your treatment options and guiding you through your surgical journey with expertise and compassion.