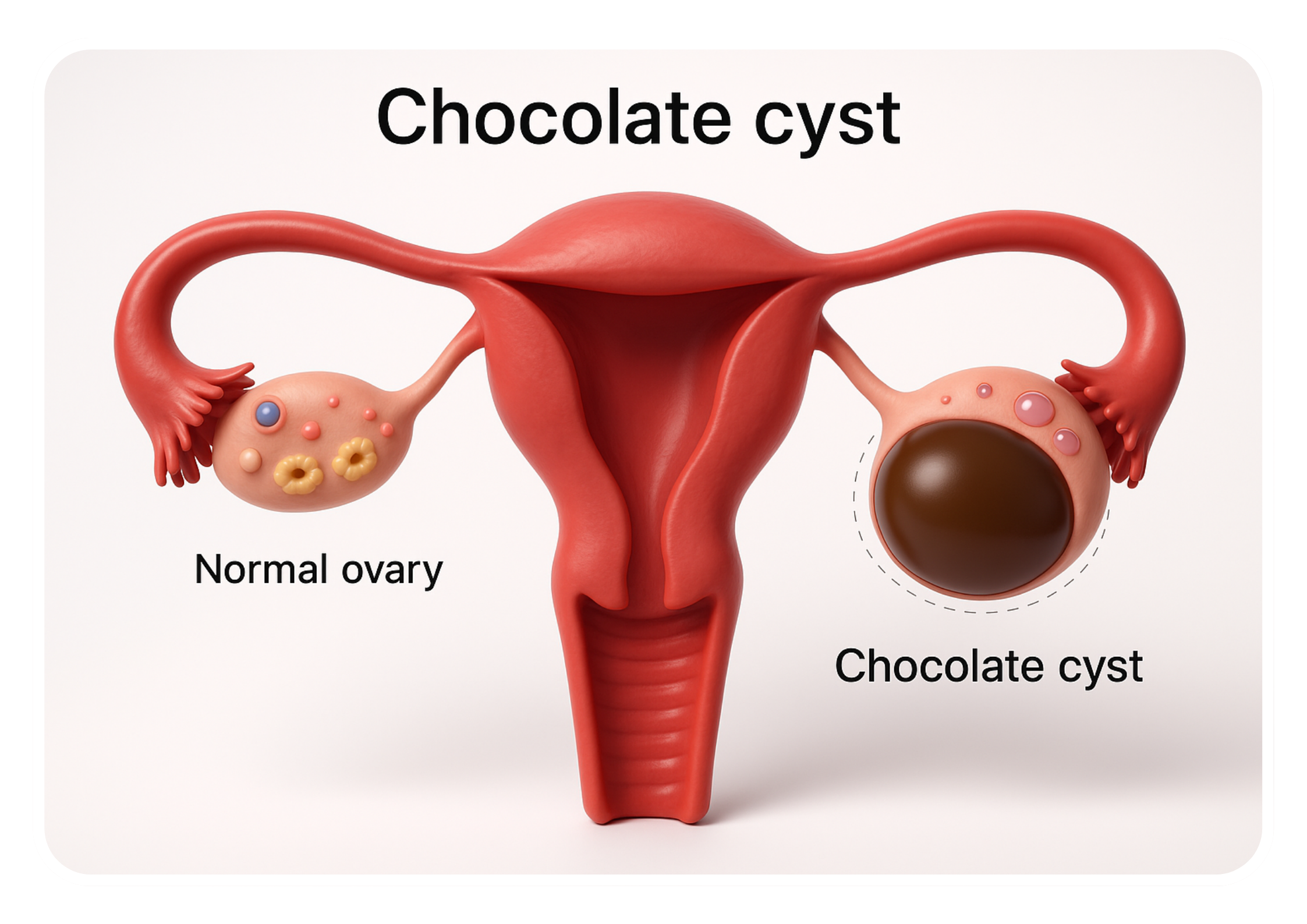
Indications
Laparoscopic chocolate cystectomy is indicated for women with symptomatic ovarian endometriomas, including:
- Pelvic pain
- Dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation)
- Dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse)
- Infertility
- Ovarian cysts detected on imaging studies (ultrasound, MRI)
Surgery may be considered when conservative management options, such as hormonal therapy or pain management, have been ineffective or if there are concerns about cyst size, location, or risk of complications.
Preoperative Evaluation
Before undergoing laparoscopic chocolate cystectomy, patients typically undergo a comprehensive preoperative evaluation, including:
- Pelvic Examination: To assess the overall reproductive health.
- Imaging Studies: Such as transvaginal ultrasound or MRI to visualize the endometriomas and other pelvic structures.
- Assessment of Symptoms and Fertility Goals: To tailor the surgical approach and discuss potential outcomes.
Preoperative counseling is essential to discuss the procedure, risks, benefits, and alternatives, as well as to address patient concerns.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: Laparoscopic chocolate cystectomy is performed under general anesthesia in an operating room equipped for laparoscopic surgery.
- Incisions: Several small (typically 0.5 to 1 cm) incisions are made in the abdomen, usually around the belly button and lower abdomen.
- Trocar Placement: Trocars (hollow tubes) are inserted through the incisions to provide access for the laparoscope and specialized instruments.
- Visualization: A laparoscope is inserted through one of the trocars to provide a magnified view of the pelvic organs, including the ovaries and endometriomas. Carbon dioxide gas is used to inflate the abdominal cavity, creating space for visualization and instrument manipulation.
- Cystectomy: The endometriomas are identified, dissected, and carefully excised from the ovarian tissue using specialized laparoscopic instruments. The cyst wall is meticulously removed to minimize the risk of recurrence and to preserve ovarian function.
- Hemostasis and Closure: After cyst removal, any bleeding vessels or defects in the ovarian tissue are carefully inspected and controlled. The ovaries are then inspected to ensure hemostasis and proper closure of the ovarian cortex. The small incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue, and dressings may be applied.
Advantages
- Minimally Invasive: Laparoscopic chocolate cystectomy involves smaller incisions, resulting in less postoperative pain, reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
- Preservation of Ovarian Function: The goal of laparoscopic cystectomy is to preserve ovarian function and fertility by removing endometriomas while sparing healthy ovarian tissue. This is particularly important for women of reproductive age who wish to preserve their fertility.
- Symptom Relief: Laparoscopic cystectomy can provide significant relief of symptoms associated with ovarian endometriomas, including pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, and infertility.
Considerations
- Ovarian Reserve: Laparoscopic chocolate cystectomy carries the risk of inadvertently damaging healthy ovarian tissue during cyst removal, which may affect ovarian reserve and future fertility. Surgeons should take precautions to minimize damage to healthy ovarian tissue and preserve ovarian function.
- Risk of Recurrence: Despite complete cyst removal, there is a risk of recurrence of endometriomas following laparoscopic cystectomy. Close follow-up and ongoing management are essential to monitor for recurrence and manage symptoms as needed.
- Surgical Expertise: Laparoscopic chocolate cystectomy requires specialized training and expertise in laparoscopic techniques and the management of endometriosis. Surgeons should be proficient in minimally invasive surgery and familiar with the nuances of ovarian cystectomy to ensure optimal outcomes.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic chocolate cystectomy is an effective surgical option for the treatment of symptomatic ovarian endometriomas, offering the advantages of minimally invasive surgery, preservation of ovarian function, and symptom relief. When performed by experienced surgeons in appropriately selected patients, laparoscopic cystectomy can provide significant benefits in terms of symptom management and reproductive outcomes. At Bliss IVF, we ensure that our patients receive the highest standard of care, tailored to their specific needs and conditions, providing comprehensive support throughout their treatment journey.