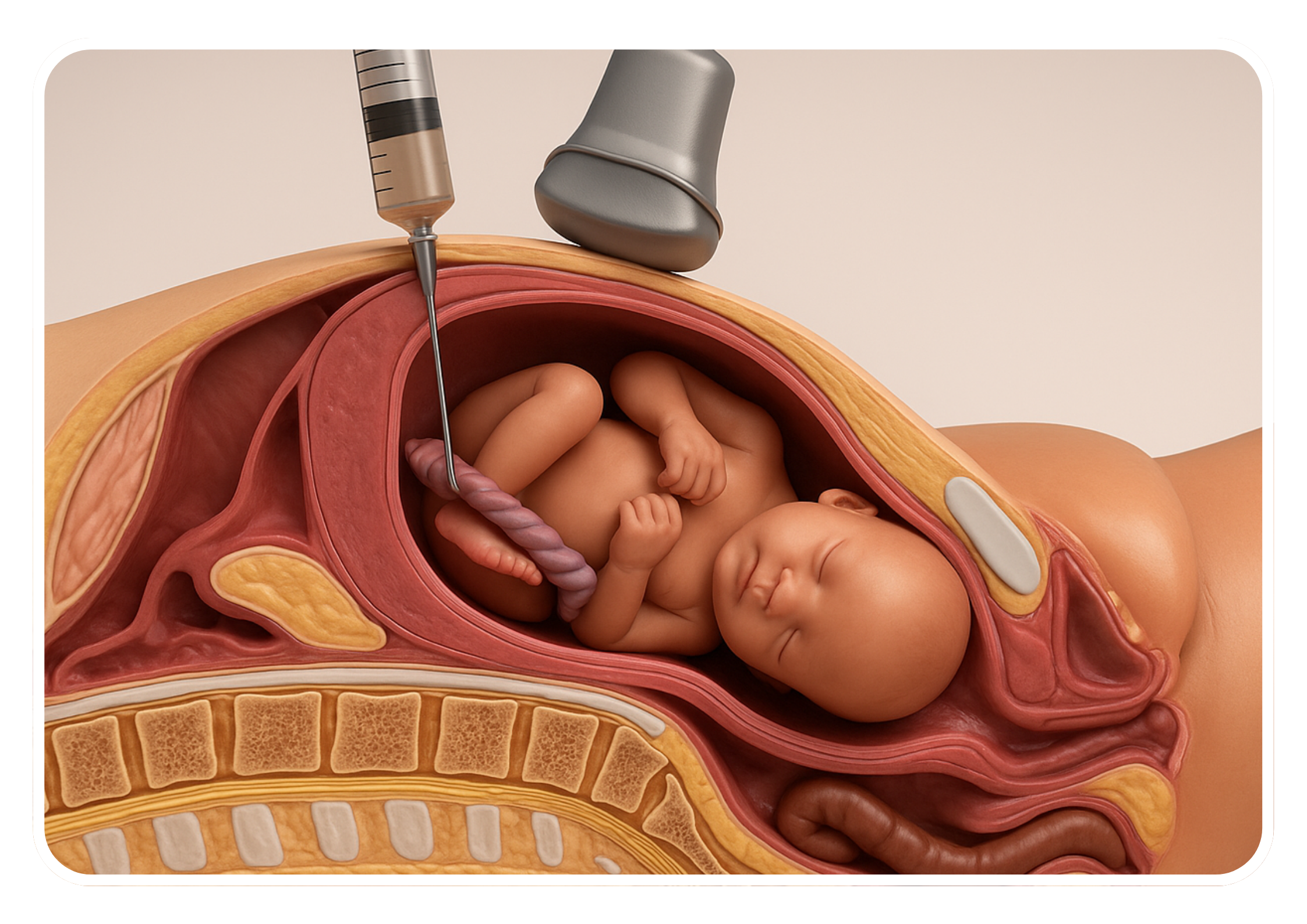
Fetal Reduction
Fetal reduction, also known as selective reduction, is a medical procedure performed during a multiple pregnancy (such as twins, triplets, or higher-order multiples) to reduce the number of fetuses in the uterus. This procedure is typically considered when the pregnancy involves more fetuses than can be safely carried to term, or when there are significant risks to the health of the mother or remaining fetuses.
Book Appointment