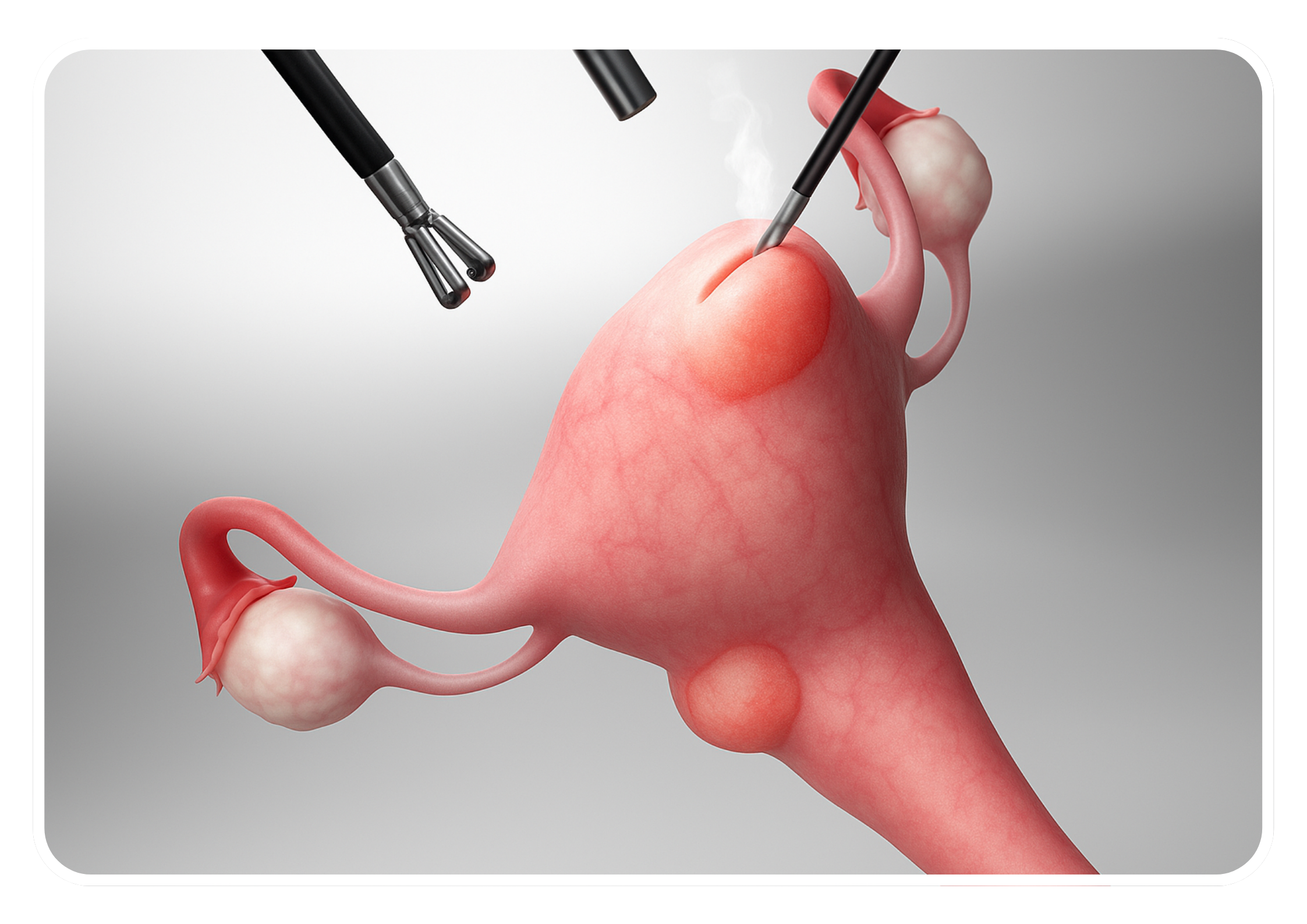
Indications
Laparoscopic myomectomy may be recommended for women with symptomatic uterine fibroids who desire preservation of their uterus and fertility. Indications for myomectomy include:
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Menorrhagia): Excessive menstrual bleeding that affects quality of life.
- Pelvic Pain or Pressure: Discomfort or pain in the pelvic region due to fibroids.
- Urinary Frequency or Urgency: Frequent or urgent need to urinate caused by pressure from fibroids on the bladder.
- Infertility or Recurrent Pregnancy Loss: Associated with fibroids impacting fertility or causing pregnancy loss.
- Enlarged Uterus or Visible Fibroids: Detected on imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI.
Preoperative Evaluation
Before undergoing laparoscopic myomectomy, patients typically undergo a comprehensive preoperative evaluation, including:
- Pelvic Examination: Physical assessment of the pelvic region.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound or MRI to visualize fibroids and assess their size, location, and number.
- Assessment of Symptoms and Fertility Goals: Understanding the patient’s symptoms and desire for future fertility.
- Preoperative Counseling: Discussion of the risks, benefits, and alternatives to myomectomy, addressing any patient concerns.
Surgical Technique
Laparoscopic myomectomy is performed under general anesthesia in an operating room equipped for laparoscopic surgery. The procedure involves the following steps:
- Anesthesia: The patient is placed under general anesthesia.
- Incisions: Several small (typically 0.5 to 1 cm) incisions are made in the abdomen, usually around the belly button and lower abdomen.
- Trocar Placement: Trocars (hollow tubes) are inserted through the incisions to provide access for the laparoscope and specialized instruments.
- Visualization: A laparoscope is inserted through one of the trocars to provide a magnified view of the pelvic organs and fibroids. Carbon dioxide gas is used to inflate the abdominal cavity, creating space for visualization and instrument manipulation.
- Dissection: The surgeon uses specialized laparoscopic instruments to dissect and isolate the fibroids from the surrounding uterine tissue. Techniques such as enucleation, morcellation (cutting the fibroids into smaller pieces), or traction may be used to remove the fibroids while minimizing damage to the uterus.
- Closure: After all fibroids have been removed, the uterine defects are closed with sutures or surgical glue to promote healing and reduce the risk of complications.
- Hemostasis: Hemostasis (control of bleeding) is ensured throughout the procedure using electrocautery, sutures, or other hemostatic techniques.
- Removal: Once the procedure is completed, the laparoscopic instruments are removed, and the small incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue. Dressings may be applied, and the patient is typically monitored in the recovery area before being discharged home.
Advantages
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions result in less postoperative pain, reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
- Preservation of Fertility: By preserving the uterus, laparoscopic myomectomy allows women to retain their fertility and reproductive options, including future pregnancies.
- Improved Cosmetic Outcomes: The smaller incisions used in laparoscopic surgery result in less visible scarring and improved cosmetic outcomes compared to open surgery.
Considerations
- Patient Selection: Laparoscopic myomectomy is generally suitable for women with symptomatic fibroids who desire uterine preservation and are suitable candidates for minimally invasive surgery.
- Fibroid Characteristics: The size, location, and number of fibroids may influence the feasibility and complexity of laparoscopic myomectomy. Large or numerous fibroids, particularly those located deep within the uterine wall, may pose technical challenges during surgery.
- Surgical Expertise: Laparoscopic myomectomy requires specialized training and expertise in laparoscopic techniques. Surgeons should be proficient in minimally invasive surgery and familiar with the nuances of myomectomy to ensure optimal outcomes.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic myomectomy is an effective surgical option for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids while preserving the uterus and fertility. When performed by experienced surgeons in appropriately selected patients, laparoscopic myomectomy offers the advantages of minimally invasive surgery, reduced morbidity, and improved patient outcomes.
At Bliss IVF, our team of skilled surgeons and healthcare providers is dedicated to offering the highest standard of care. We are committed to helping you understand your treatment options and guiding you through your surgical journey with expertise and compassion.