Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
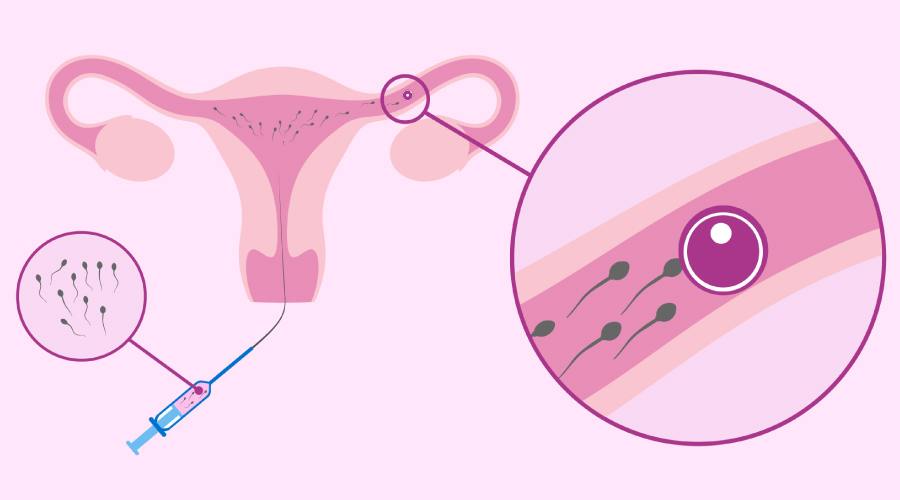
IUI stands for intrauterine insemination and is a form of artificial insemination used to treat infertility.
When your ovary produces one or more eggs to be fertilized, washed, and concentrated sperm is inserted directly into your uterus.
The goal of intrauterine insemination is for sperm to swim into the fallopian tube and fertilize an egg waiting to be fertilized, resulting in pregnancy. IUI can be used with your regular cycle or with fertility medicines, depending on the cause of infertility.
Infertility is no longer a problem because of advancements in reproductive technology. Fertility treatments make it possible for anyone to have a child at any age.
IVF/IUI is the first thing that comes to mind when people think of assisted reproductive technologies. IUI is also one of the most rapidly evolving procedures, and it is also much less expensive than IVF. Even if you need numerous treatment cycles, the overall cost will be lower.
How IUI is different from IVF?
Here are some key distinctions between IUI and IVF:
- In IVF, fertilization takes place outside of the human body, in a petri dish. In IUI, washed sperm is injected into the uterus of the woman.
- IUI has a success rate of about 10-20% for a single cycle, while IVF has a success rate of about 65-72 percent.
- A cycle of IUI is much less expensive than an IVF cycle.
What are the steps for IUI?
- Your spouse must accompany you on the day of the insemination and provide a semen sample. If you choose a sperm donor, the donor sample will be thawed and ready for operation before you arrive.
- The retrieved sperm sample is cleansed to ensure that only high-quality sperm remain and that all other contaminants are removed.
- In your cervix, a catheter containing cleansed sperm is implanted, and the filtered semen is inserted into your uterus.